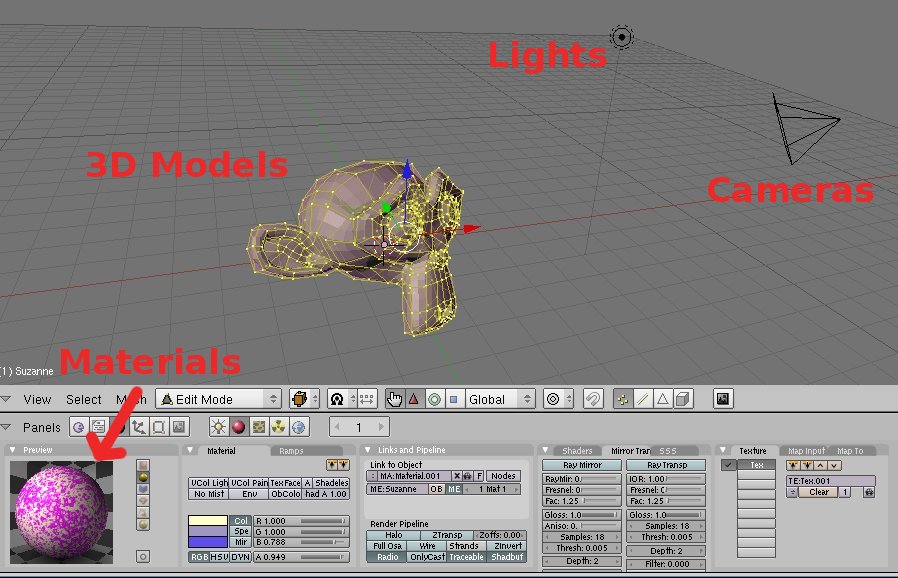

 |
 |
| Download this simple scene | |
 |
 |
|
Ray-tracing
|
Rasterization
|
 |
 |
Vertex
processing
|
 |
Primitive
processing
|
 |
Rasterization
|
 |
Fragment
processing
|
 |
Pixel
processing
|
 |
Vertex
and fragment processing now programmable!
Why is it usefull?
|
| // GLSL version #version 330 // Vertex attributes (given by glVertexAttribPointer(...)) layout(location = 0) in vec3 vertexPosition_modelspace; layout(location = 1) in vec3 vertexColor; // Output data: will be interpolated for each fragment out vec3 fragmentColor; // ModelViewProjection matrix (constant for the whole mesh) uniform mat4 MVP; void main() { // Output position of the vertex, in clip space : MVP * position gl_Position = MVP * vec4(vertexPosition_modelspace,1); // The color of each vertex will be interpolated // to produce the color of each fragment fragmentColor = vertexColor; } |
// GLSL version #version 330 // Interpolated values from the vertex shaders in vec3 fragmentColor; // Ouput data out vec3 color; void main() { // Output color = color specified in the vertex shader, // interpolated between all 3 surrounding vertices color = fragmentColor; } |
| Vertex
shader |
Fragment
shader |

 |
Programmable
stages
|
| PREVIOUS:
EXERCICE02 |
NEXT:
EXERCICE03 |